Security & Fraud
Different Types of Fraud

Steps You Can Take to Protect Yourself Online
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Create strong passwords for your accounts, and avoid using the same password across multiple sites. Consider using a reputable password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Also known as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Whenever possible, enable 2FA for your online accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification (like a code sent to your phone) in addition to your password.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that your operating system, antivirus software, web browsers, and other applications are always up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Be Cautious with Personal Information: Avoid sharing sensitive information such as your full birthdate, Social Security number, or financial details unless absolutely necessary and through secure channels.
- Use Secure Connections: When browsing the web, make sure the websites you visit use HTTPS (look for the padlock icon in the address bar). Avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities without using a virtual private network (VPN) for added security.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of unsolicited emails, messages, or phone calls asking for personal information or urging you to click on links or download attachments. Verify the sender’s identity before taking any action.
- Review Privacy Settings: Regularly review and adjust the privacy settings on your social media accounts and other online services to control who can see your information.
- Backup Important Data: Regularly back up important files and data to an external hard drive or secure cloud storage service. This can protect your data in case of hardware failure, ransomware, or other issues.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about current online threats and best practices for online security. Educate family members, especially children, about safe internet usage.
- Use Security Software: Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices to help detect and protect against malicious software and threats.
By following these steps, you can significantly enhance your online security and reduce the risk of falling victim to cyber threats.
Fraud Text Examples
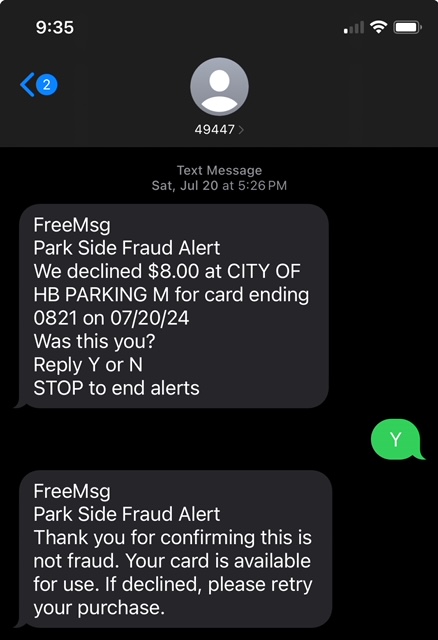
LEGITIMATE TEXT
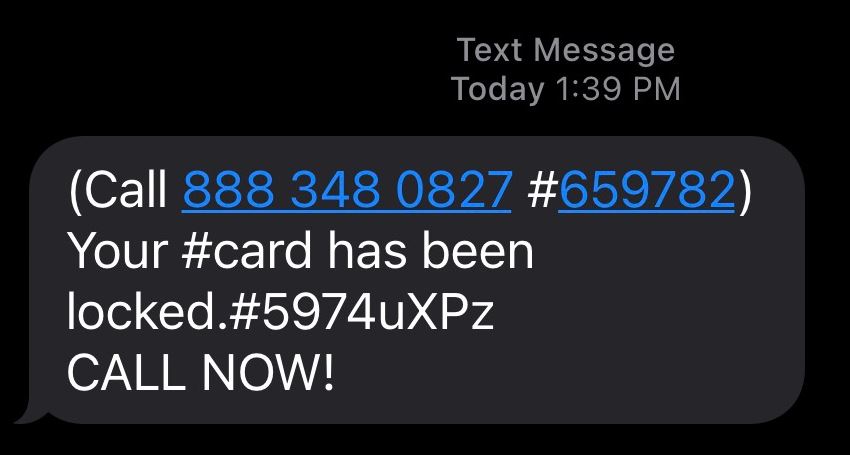
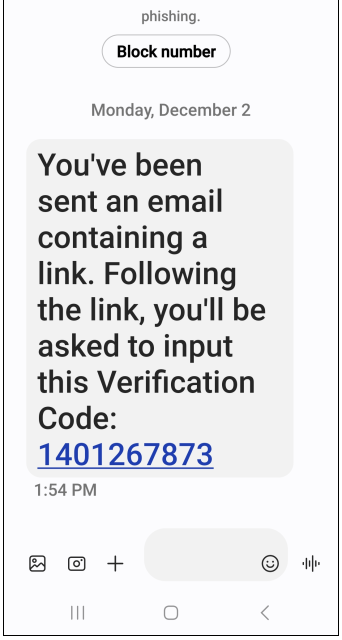
FRAUDULENT TEXTS
Things to notice in legitimate text message:
- “Park Side Fraud Alert” – use of actual credit union name
- Details of attempted transaction – verify your specific card activity
- “Reply Y or N” – simple approval or denial of suspected charge
- No link or verification code – not required to visit another site or enter information
Call to Action
If you believe that your information may have been compromised or if you have been the victim of a scam, please use the resources listed below:
Contact Park Side Credit Union as soon as possible
Flathead – 406.862.2652 | Missoula – 406.728.4475
After hours – 866.820.4858
Contact the Federal Trade Commission – 877.438.4338




